AI in Drupal: Get Started with the AI Module
Bringing AI Capabilities to Your Drupal Site with the AI Module
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly changing how we approach content creation, content delivery, and user interaction on the web. The AI module for Drupal, compatible with the latest Drupal 11 release, provides a structured, extendable foundation that lets site builders and developers incorporate OpenAI and other Large Language Models (LLMs) directly into the Drupal admin interface, content workflows, and front-end experiences.
The AI module integrates directly with Drupal’s core systems and editorial experience. One of its most visible features is the ability to generate content from within entity editing forms, including WYSIWYG fields. However, its functionality goes beyond editor assistance. It allows site builders to configure reusable prompt templates across different content types, define input mappings, and guide content generation in a way that respects Drupal’s structured approach. The AI module makes these capabilities more accessible in a Drupal-native way.
In this blog, we’ll explore the core features of the module, walk through some real-world use cases, and explain how to set it up on your own Drupal site.
A Centralized AI Interface Built for Drupal
Once installed and configured, the AI module provides a centralized interface for managing AI backends such as OpenAI, LocalAI, and HuggingFace. You can switch between providers and models, set API keys, and fine-tune options like temperature, maximum tokens, and frequency penalties depending on the behavior you want from the AI.
To use a provider like OpenAI, you first need to create an account at openai.com. From your account dashboard, you can generate an API key, which is required to connect your Drupal site to OpenAI’s services. This key is entered in the AI module’s configuration settings to authenticate requests and enable content generation directly from the Drupal interface.
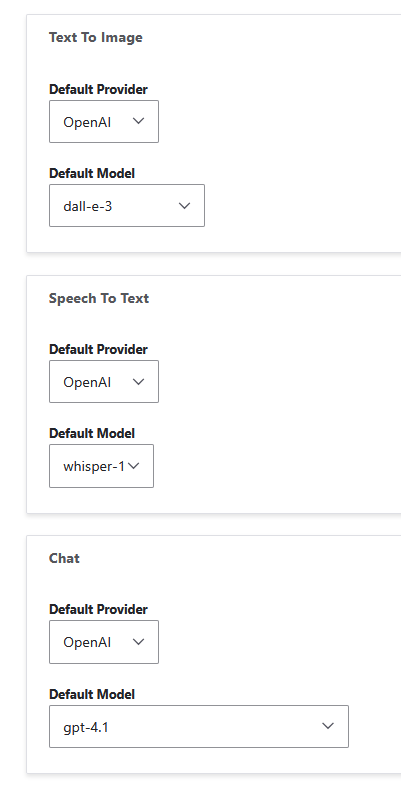
The module's configuration is available under Configuration > AI > AI Default Settings, where settings are organized by backend and submodel. For example, you might choose gpt-4 for detailed summaries or complex content generation, and use gpt-3.5-turbo for faster, more lightweight tasks like rewriting metadata or assisting with short text fields. These model choices appear throughout the module, allowing you to match the right tool to the task, whether you're generating product descriptions or translating blog content.
The AI module also includes a set of default prompt templates and actions designed for typical content tasks. These are stored as configuration entities in Drupal, making them easy to duplicate, modify, and extend. You can change the default wording of prompts, adjust model settings, or target specific content fields, all through Drupal’s familiar configuration interface. This makes the AI integration highly adaptable to a range of editorial and content generation workflows.
Assisted Content Creation for Editors and Site Builders
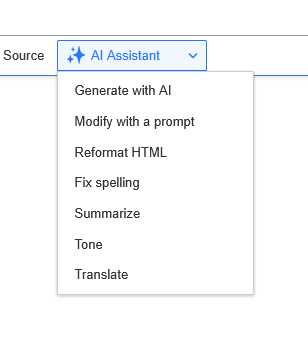
One of the most immediate use cases is AI-assisted content creation. Once the module is installed, a new “AI Assistant” tab appears in entity editing interfaces. This allows editors to select a predefined action like “Summarize,” “Generate with AI,” or “Fix spelling,” and run it against a text field.
For example, when editing a node, an editor can select a prompt that says “Generate an introduction for this article” and apply it to the body field. The module will submit the existing content (or selected field) to the chosen LLM and return a suggestion directly in the Drupal interface. The text is editable, and nothing is saved until the user confirms.
To enable this functionality inside text areas like the Body field, site administrators need to add the “AI Assistant” button to their CKEditor configuration. This can be done under Configuration > Content Authoring > Text formats and editors, by editing the desired text format (such as “Full HTML”) and including the AI Assistant button in the active toolbar. Once added, users will see the AI icon in their WYSIWYG editor, allowing them to trigger prompts directly from within the text field.
These features make it possible for editors and site builders to manage all writing, editing, and refinement tasks directly within Drupal. There’s no need to copy and paste between ChatGPT or other tools. Prompts can be triggered exactly where content is being created, with suggestions returned in place. This saves time and reduces context switching while keeping content creation embedded in the same environment where it’s ultimately published.
Since prompts are stored as configuration entities, they can be fully customized to align with your organization’s editorial tone or specific content needs. You can create your own prompt actions, adjust their wording, or even add role-based access controls. You can also restrict which AI models are available for certain tasks, giving you a flexible and governed AI experience inside the Drupal admin.
Automating Translation and Localization Workflows
Another powerful feature of the AI module is its ability to support translation workflows directly within the Drupal admin interface. You can generate multilingual content without switching between Drupal and external tools like ChatGPT.
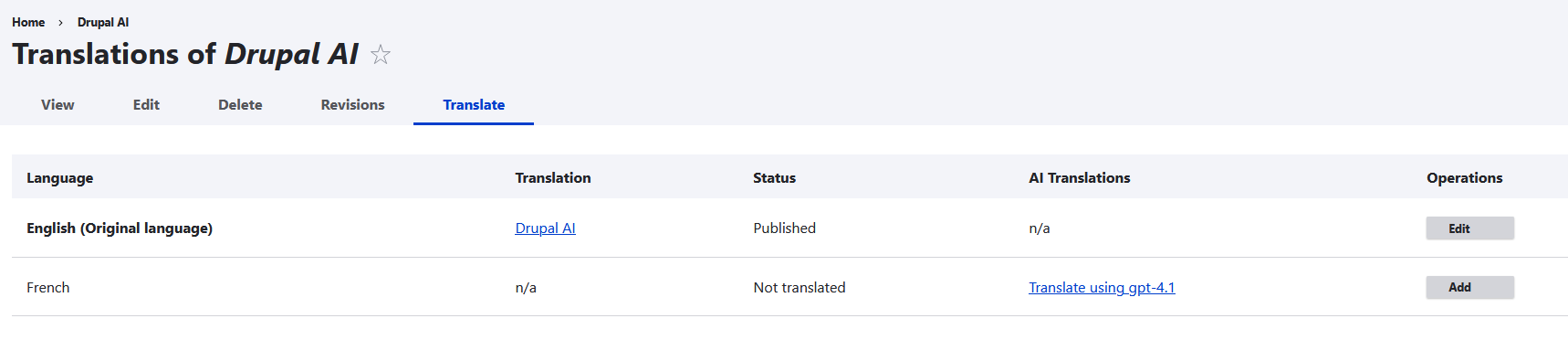
When managing translations for a node, a new “AI Translations” column appears next to each language. If a translation does not yet exist, a link such as “Translate using gpt-4.1” (or another model you’ve configured) will appear. Clicking it will trigger the AI module to generate a translated version based on your selected model and prompt configuration.
You can also define your own translation prompts to reflect your editorial standards and match your desired tone, whether that’s formal, regionally adapted, or simply fast and functional. This helps accelerate time-to-publish for multilingual websites, especially when official translations may take time or are handled by different teams.
Since the AI module is integrated with Drupal’s entity and field systems, it understands the structure of your multilingual content. It ensures the translated version is saved in the correct language context, and it leaves the original language untouched. Editors can review and edit the AI-generated content before saving, maintaining full control over the quality of the translation.
This functionality streamlines multilingual publishing and enables editors to work faster while staying entirely within the Drupal interface.
AI Search for Smarter Content Discovery
Traditional Drupal search solutions like Search API rely on indexing specific fields and performing keyword-based matching. They work well when users search for exact terms or predefined filters, but they often miss the nuance behind a user’s intent. For example, a query like “ways to reduce energy use” may not return a result titled “Improving your building’s efficiency” unless those exact terms appear in the content or metadata.
The AI module introduces a new way to approach search by using vector embeddings, which represent the meaning of content and user queries. Instead of matching words, it matches ideas. This makes it possible to surface relevant content even when phrased differently, helping users discover what they’re looking for, even if they don’t use the exact keywords.
You can use this approach to build smarter internal search tools, return similar content suggestions after a blog post, or power help widgets that guide users to relevant documentation. Since it integrates directly into Drupal, you can choose which content types or fields to index, how embeddings are generated, and how results are returned, all through the AI module’s configuration interface.
While promising, this functionality is still in an experimental phase. It may not yet replace traditional search tools for all use cases, and should be tested carefully before deploying on production sites. While Search API remains a reliable and widely-used solution for structured, filterable search interfaces, the AI module complements it by enabling a new kind of relevance: search experiences based on meaning rather than exact terms.
AI Assistant Chatbots and Front-End Interactions
The AI module also supports front-end experiences like conversational interfaces and AI-powered assistants. With a bit of configuration, you can deploy a chat component on your site that helps visitors navigate your content, answers basic questions, or generates content variations based on visitor preferences.
For instance, a chatbot can use content from your site to respond to user questions in real time, pulling data from nodes, views, or session-based user context. You might also guide users through a product or service flow by prompting the AI to respond based on previous answers or selections.
These assistants are built using the same prompt system and model configuration used in the admin UI, so there’s no need for a separate integration. Prompts can be adjusted from the Drupal admin to change tone, output format, or AI behavior. Developers can extend this by connecting AI actions to blocks, forms, or JavaScript-based interactions, enabling a variety of use cases without complex custom code.
This kind of interaction makes it possible to offer smart, context-aware help directly on the site, powered by your existing Drupal content.
AI in Drupal is Just Getting Started
The AI module makes it easier to experiment with generative AI in real Drupal projects. By bringing model access into the admin interface, field widgets, and content workflows, it unlocks a range of features that are both powerful and user-friendly.
From improving content quality to accelerating translation, and from customizing the front-end to creating new user experiences, AI is beginning to play a practical role in how content is built and delivered in Drupal.
While the module is still evolving, its architecture is stable and already supports a wide range of use cases. If you're interested in bringing AI into your Drupal site, this is a solid foundation to build on.
At Monarq, we can help you plan and integrate AI functionality into your existing or future Drupal projects. Whether you're looking to configure the AI module, match it with your content model, or explore advanced use cases, we’d love to hear from you.